How to mount RCC NOR (fs0)
:::info Prerequisite of using flashit is RCC NOR mounted in /dev/fs0
When for example ifs.root-stage2 is damaged, RCC is still booting but NOR is not mounted in /dev/fs0 automatically.
:::
To check, run ls -al /dev/fs* and you should see a list like:
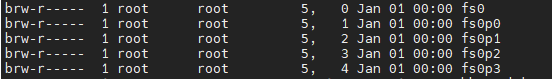
If this list is empty then run:
/usr/bin/stop_efs_driver.sh
/sbin/devf-generic -s0x08000000,64M,,,128k,2,1 -r -D -P 1
Check ls -al /dev/fs* again. If fs0 is there then you can run /usr/bin/flashunlock and /usr/bin/flashit. Remember, fs0 is mounted only untill next reboot.
:::tip If /usr/bin/flashunlock and /usr/bin/flashit are not available insert m.i.b. SD into SD1 slot and try to run /net/mmx/fs/sda0/apps/sbin/flashunlock and /net/mmx/fs/sda0/apps/sbin/flashit
Alternatively, you can unpack attached Flashit Flashlock.rar onto FAT32 formatted SD and run /net/mmx/fs/sda0/flashunlock and /net/mmx/fs/sda0/flashit
:::
Description of devf-generic can be found here:
DESCRIPTION=arm generic flash
DATE=2013/05/09-12:02:26-EDT
STATE=stable
HOST=pspbuildvm
USER=pspbuild
VERSION=650SP1-3575
TAGID=5189
%C - Fast Flash File System v3 (POSIX compatible)
%C [-aclrvV] [-b priority] [-f verifylevel] [-i index]
[-m mountover] [-p backgroundpercent[,superlimit]]
[-s baseaddress[,windowsize[,arrayoffset[,arraysize[,unitsize[,buswidth[,interleave]]]]]]]
[-t threads] [-u updatelevel] [-w buffersize]
Options:
-a disables all automounting/enumeration of partitions
-A all partitions are resmgr_attach() with the AFTER flag.
-E do not daemonize and exit on EBADFSYS with partition num + 1
-l list available flash databases and exit
-r enable fault recovery of dangling extents chains, partial
reclaims, dirty extent headers and damaged extent pointers
-R mount read-only
-v display verbose info
-V display filesystem and MTD version information
-b priority enable background reclaim at priority
(low and high are system dependant)
-f verifylevel enable flash verify (def.=0, 0=meta, write=1, erase=2, all=3)
-i arrayindex[,partindex]
set first array index and first partition index for multiple
drivers (def.=0,0 (for /fs0p0), min=0, max=15)
-m mountover
override default mountpoints assigned to file systems
formatted with an empty (i.e. "") mountpoint, mountover can
include two %X format specifiers (as in printf) for the socket
index and the partition index respectively
(def.=/fs%Xp%X)
-p backgroundpercent[,superlimit]
set parameters like background reclaim percentage trigger
for stale space over free space, and superseded extent limit
before reclaim (def.=100,16)
-s baseaddress[,windowsize[,arrayoffset[,arraysize[,unitsize][,buswidth[,interleave]]]]]
set socket options (normally base physical address, window
size, array offset, array size, unit size, bus width and
inter-leave). But the format is left flexible for socket
services with customized drivers.
the program timeout and erase suspend timeout can be specified
behind interleave to avoid infinite loop (recommended 10000,100).
-t hi_water[,lo_water[,max]]
set the attribute of thread pool (increment=1, def.=4,2,100,
0<hi_water<max, 0<=lo_water<=hi_water, hi_water<max<=100)
-u updatelevel set time Update Level (def.=0, 0=never, 1=file, 2=parent)
-w buffersize set append buffer size (def.=512, 0=disable)
-L limit set flash program retry limit
-e <arg> enumerate partitions only. If <arg> is a number, then automount
the first <arg> partitions. If <arg> is a string, it is taken
as a colon-separated list of exact pathnames to mount, if found.
-d log set log method
-k blksz set extent cache block size, default is 128k
-o file_max set the maximum number of files to cache, default is 64
-x enable software ECC mode.
-D enable automatic detection of ECC mode.
-S sector_erase_latency
set simulated sector erase latency in ms (max = 10000).
-P lock_mode
set protection mode for Spansion compatible device (def.=0,
0=no lock, 1=persistent lock mode, 2=dynamic lock mode)
-T max_erase_diff
set threshold value (maximum erase count - minimum erase count
in a partition) to trigger wear levelling, default value is
two times of sector number in the partition. Typically,
for very large partition containing more than 1000 sectors,
this option should be used to specify a threshold
(for example, 1000) to make sector erase counts more evenly
distributed across the entire partition.
Examples:
%C -w0
Starts a flash filesystem with no append buffering.
%C -b5 -u2 -r
Starts a flash filesystem with background reclaim process enabled and
most POSIX semantics with an initial fault recovery when automounting.
Mountpoints:
This is for the default mountpoint index...
/fs0p0 structured flash filesystem mountpoint
/dev/fs0 socket mount mountpoint
/dev/fs0p0 raw partition mountpoint
%C -e 2
Starts the flash filesystem, automounting /dev/fs0p0, /dev/fs0p1, and /dev/fs0p2. Any
remaining partitions are only enumerated (entries created under /dev, but
no mounted filesystem).
Notes:
Hard links and access times are not supported with the flash filesystem.
Symbolic links, modification and change times are supported.
\